Quantitative Analysis of Ki67, a Prognostic Biomarker in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
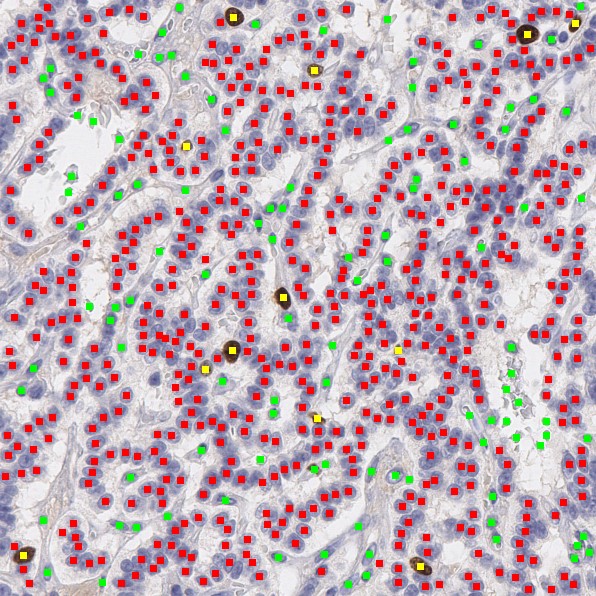
Abstract
Summary:
- Ki67 Labeling Index (LI) is the preferred method of establishing grade for GEP-NETs
- Several approaches to measuring Ki67 LI exist in practice
- Machine learning offers an attractive method for calculating Ki67 LI
- Pathologists need to be accurate and precise when performing pixel-based labeling of training data
- While strict guidelines for Ki67 LI in GEP-NETs do not exist, expert opinion and analogy to other tissues is helpful
- KiNet is a single-stage deep-learning-based detection and classification pipeline with performance at or above the state of the art
Date
May 19, 2022 2:00 PM — 3:00 PM
Event
The Image Guided Cancer Therapy Research Program Seminar Series
Location
MD Anderson Cancer Center (Virtual)